Abstract statistical pattern underlies all knowledge
/I’ve long thought specific visual patterns can trigger a recollection in the mind. And last month reading Smith and Kosslyn's Cognitive Psychology, I saw this explanation….and nearly jumped out of my chair.I fully subscribe to the idea that a statistical pattern is the mechanism for how the mind links and connects recollection….and in time, we may capture neurons firing/neurons not firing 11101010000 – ones and zeros, and be able to play back a science fiction film version of a recent experience.
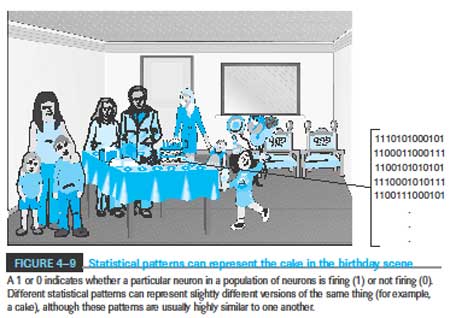
“Some researchers have argued that an abstract descriptive representational format underlies all knowledge. But the brain is a complex system, and knowledge is used in many ways; representations play many roles in the myriad processes that constitute cognition. It is implausible that a single format would serve all these roles; it is much more likely that multiple formats—images, feature detectors, amodal symbols, and statistical patterns—are required.
Because the neurons representing the statistical pattern are conjunctive neurons, all neurons are linked and become associated with the neurons that represent the statistical pattern. Each element in the statistical pattern develops associations back to the image and feature units that activated it.
Together, this sequence of processing phases establishes a multilevel representation of the scene as it is perceived. It is possible, as it were, to “run the film backward.” In a process known as simulation, a statistical pattern can reactivate image and feature information even after the original scene is no longer present. Whereas bottom-up processing through a perceptual system produces a statistical representation, top-down processing back the other way reenacts, at least partially, the original visual processing. This top-down capability allows you to generate mental images and to remember past events.”